In today’s connected world, digital threat protection is more important than ever. Cyber threats lurk around every corner, putting both businesses and individuals at risk of devastating cyberattacks. Hackers are constantly evolving their tactics, using phishing scams, ransomware, and malware to steal sensitive data, disrupt systems, and cause financial losses. Without proper cybersecurity measures, you could wake up one day to find your personal information stolen, your bank account drained, or your business crippled by an attack.
This is why digital threat protection is essential. It’s not just about installing an antivirus program—it’s about adopting strong security practices, using advanced cybersecurity tools, and staying informed about emerging threats. In this blog, we’ll break down the most common cyber threats, their risks, and the best strategies to safeguard yourself or your organization against them.
What Is Digital Threat Protection?
Understanding the Importance of Cybersecurity
Digital threat protection refers to the practices, tools, and strategies used to defend against cyberattacks that threaten personal and business data. With an increasing number of devices connected to the internet, cybercriminals have more opportunities than ever to exploit weaknesses and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Effective digital threat protection involves multiple layers of security, including firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time threat monitoring. Cybersecurity isn’t just a concern for large corporations—it’s something that every individual should prioritize. Whether you’re shopping online, using social media, or running a business, cyber threats can impact anyone.
Key Components of Digital Threat Protection
To effectively safeguard against cyber threats, a comprehensive digital threat protection strategy includes:
-
Threat detection and response: Identifying suspicious activity before it causes harm.
-
Data encryption: Ensuring sensitive data remains unreadable to unauthorized users.
-
Access controls and authentication: Using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
-
Regular software updates: Patching security vulnerabilities before hackers exploit them.
-
Security awareness training: Educating employees and individuals about potential cyber threats.
With cyberattacks becoming more sophisticated, organizations and individuals must remain proactive in protecting their digital assets.
Common Types of Digital Threats
Phishing Attacks – The Deceptive Emails That Trick You
One of the most common cyber threats today is phishing. Cybercriminals send deceptive emails, messages, or websites designed to trick users into revealing personal information, such as passwords or banking details. These messages often appear to be from legitimate sources, such as banks, social media platforms, or trusted service providers.
For example, you might receive an email that claims to be from your bank, urging you to update your password by clicking on a provided link. However, the link redirects you to a fraudulent website that steals your login credentials.
How to Protect Yourself from Phishing Attacks
-
Never click on links from unknown or suspicious emails.
-
Verify the sender’s email address before responding.
-
Enable spam filters to block phishing emails.
-
Use email authentication protocols like DMARC and SPF for business emails.
Ransomware – Holding Your Data Hostage
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on a victim’s device, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. These attacks have become increasingly common, targeting businesses, hospitals, and even government agencies.
Once ransomware infects a system, it locks files and displays a message demanding payment—often in cryptocurrency—to regain access. Paying the ransom, however, doesn’t guarantee file recovery and may encourage further attacks.
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
-
Regularly back up your data on a secure, offline storage system.
-
Avoid downloading attachments or clicking links from unknown sources.
-
Keep your operating system and software updated with the latest security patches.
-
Use reliable digital threat protection tools to detect and block ransomware.
DDoS Attacks – Crashing Websites and Networks
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack overwhelms a website or server with excessive traffic, causing it to slow down or crash. These attacks are often carried out using botnets—networks of infected computers controlled remotely by hackers.
Businesses that rely on online services, such as e-commerce websites, are prime targets for DDoS attacks, which can lead to significant revenue loss and damage to customer trust.
How to Protect Your Website from DDoS Attacks
-
Use a DDoS protection service to filter out malicious traffic.
-
Implement rate limiting to control the number of requests your server processes.
-
Deploy a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute traffic across multiple servers.
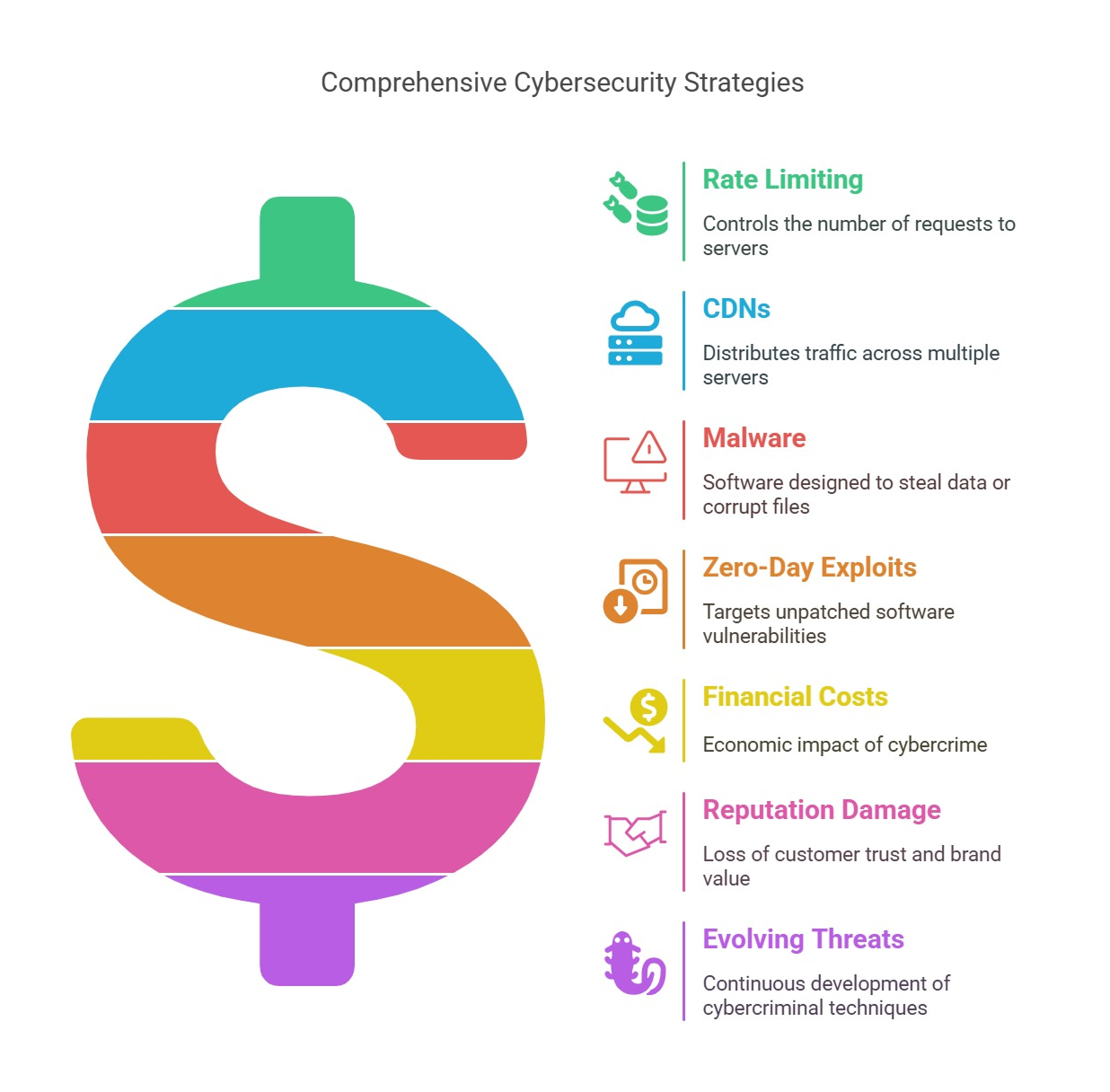
Viruses and Malware – Silent Threats Lurking in Your System
Malware is malicious software designed to steal data, corrupt files, or gain unauthorized access to a system. Viruses, trojans, spyware, and worms fall under this category. These threats often spread through infected email attachments, software downloads, or compromised websites.
How to Keep Your System Malware-Free
-
Install reputable antivirus software and enable real-time scanning.
-
Avoid downloading software from untrusted sources.
-
Regularly update your security programs and operating system.
Zero-Day Exploits – Attacks That Strike Before Fixes Are Available
A zero-day exploit targets vulnerabilities in software before developers can release a security patch. Hackers actively search for these weaknesses, using them to infiltrate systems before a fix is available.
Organizations and individuals must keep their software updated and use intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor for unusual activity.
Why Digital Threat Protection Is Essential
The Financial Cost of Cyberattacks
Cybercrime results in billions of dollars in losses every year. A single data breach can cost businesses thousands—or even millions—of dollars in fines, legal fees, and lost revenue. Small businesses, in particular, often struggle to recover from cyberattacks due to limited resources.
Reputation Damage and Customer Trust
When businesses suffer a cyberattack, customer trust can take a major hit. If sensitive data is compromised, customers may lose confidence in the company’s ability to protect their information, leading to lost business and long-term damage to the brand.
Evolving Cyber Threats
Cybercriminals continuously develop new techniques, making digital threat protection an ongoing challenge. Businesses and individuals must stay ahead of the latest threats and adapt their cybersecurity measures accordingly.
Conclusion
Digital threat protection is not just about reacting to cyberattacks—it’s about preventing them before they happen. By staying vigilant, implementing the right security tools, and educating yourself on cyber risks, you can significantly reduce the chances of falling victim to an attack.
Cyber threats will continue to evolve, but so will digital security solutions. Taking proactive measures today will protect you from financial loss, reputational damage, and unnecessary stress in the future.
You may also like this:
1. How Cybersecurity Solutions Companies Are Delivering Advanced Protection for 2025